Robust and Fast Hypothesis Verification in 3D Object Recognition |
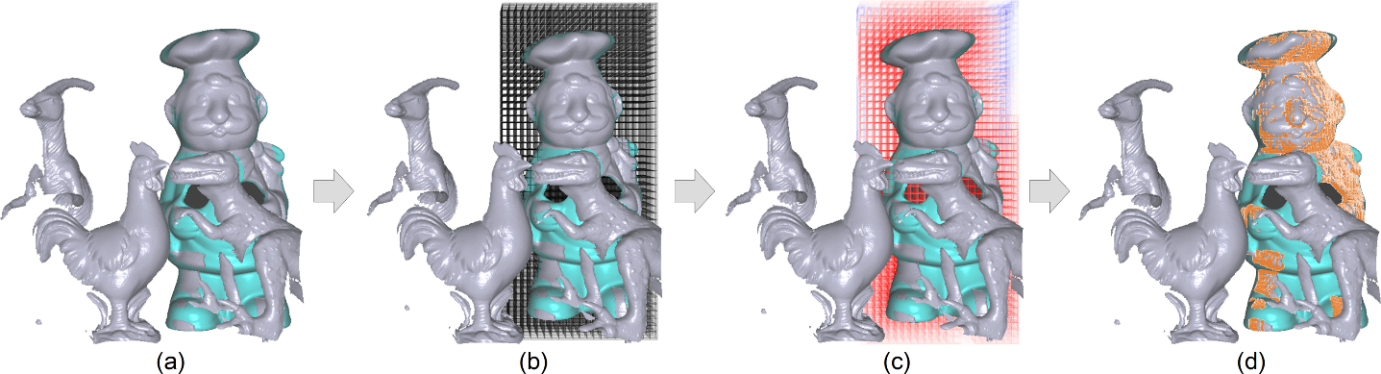
Figure 1: (a) A hypothesis to be verified, where the model (in cyan) has been transformed into the scene (in gray); (b) voxelize the model in its local object space; (c) create a distance map for the model within the voxelization; (d) identify the overlap region by utilizing the voxelization and the distance map. Note that we remove the frontal half of the voxelization in (b) and the distance map in (c) for visualization.
Abstract
3D object recognition requires generating and verifying hypothesis, where a hypothesis means a hypo thesized object together with a hypothesized pose of the object in the scene. Hypothesis verification is typically achieved by transforming the hypothesized object model into the scene based on its pose, estimating the overlap between the transformed model and the scene, and accepting the hypothesis if the overlap area is sufficiently large. This paper develops a robust and fast hypothesis verification approach to improve the recognition accuracy without slowing down its speed. Our key idea is to ident ify corresponding points in the overlap between a hypothesized model and the scene using both point po sition and normal, and to speed up the identification of corresponding points by utilizing a signed di stance transform map defined on the model's voxelization. Moreover, we estimate overlap area from the identified corresponding points more accurately based on an idea of area-weighted vertices. Experimen ts on publicly available datasets demonstrate the robustness and efficiency of our verification appro ach.Download
PDFSource Code
Results
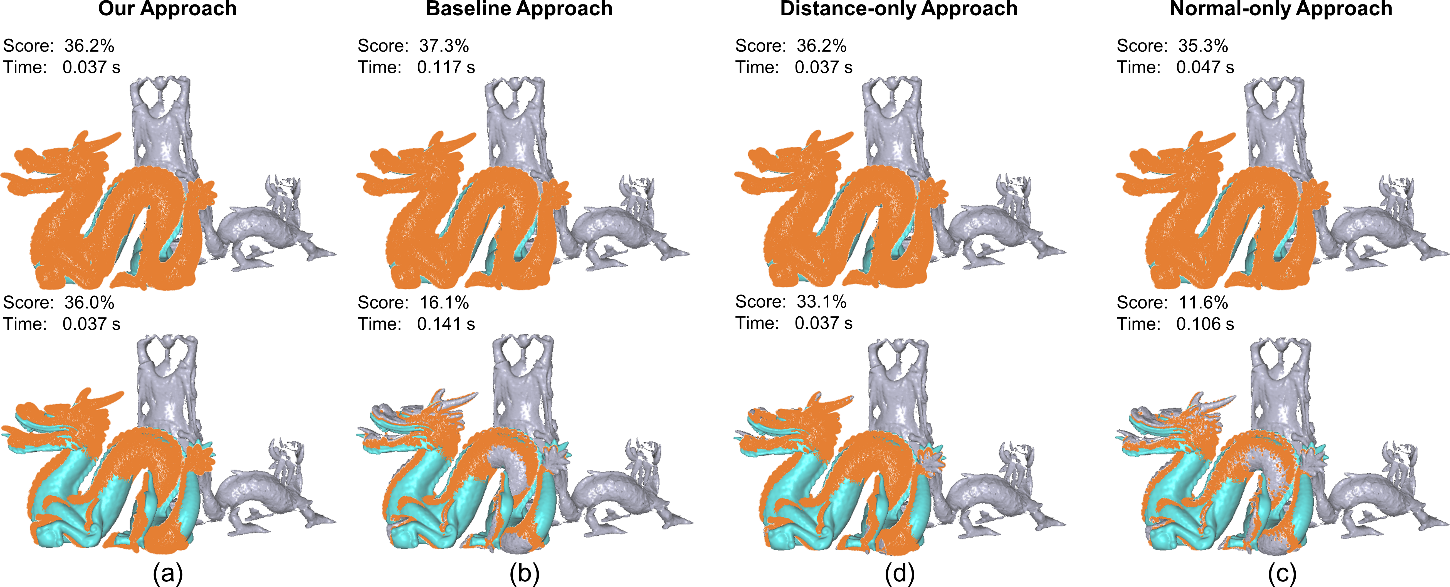
Figure 1: Verify hypotheses using (a) our, (b) baseline, (c) distance-only, and (d)
normal-only approaches for the object model is well aligned (top) and roughly aligned (bottom). The i
dentified overlap regions are colored in orange. The score and computation time are shown on the top
left corner of eachresult.
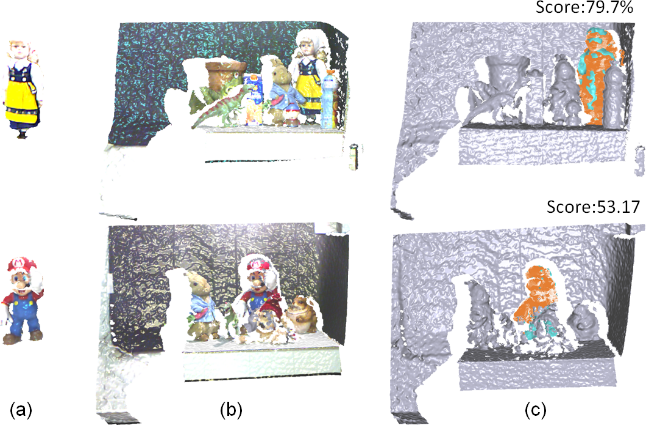
Figure 2: Evaluate our approach on scan. (a) The target scan; (b) the scene; and (c)
our verification result and the corresponding score.
Conclusion
This paper presents a volumetric approach that can improve the accuracy and speed for verifying hypotheses in 3D object recognition. The improvement on accuracy is achieved by a new measure to identify corresponding points in the overlap region and the weighted vertices approach to estimate the overlap area. The improvement on speed is achieved by building a distance transform map on each object model offline such that corresponding points can be identified simply by looking up distance values in the map. Experimental results show that our verification approach is robust to the model pose, scene point density, and object clutter, and can improve the object recognition performance better than a baseline approach.